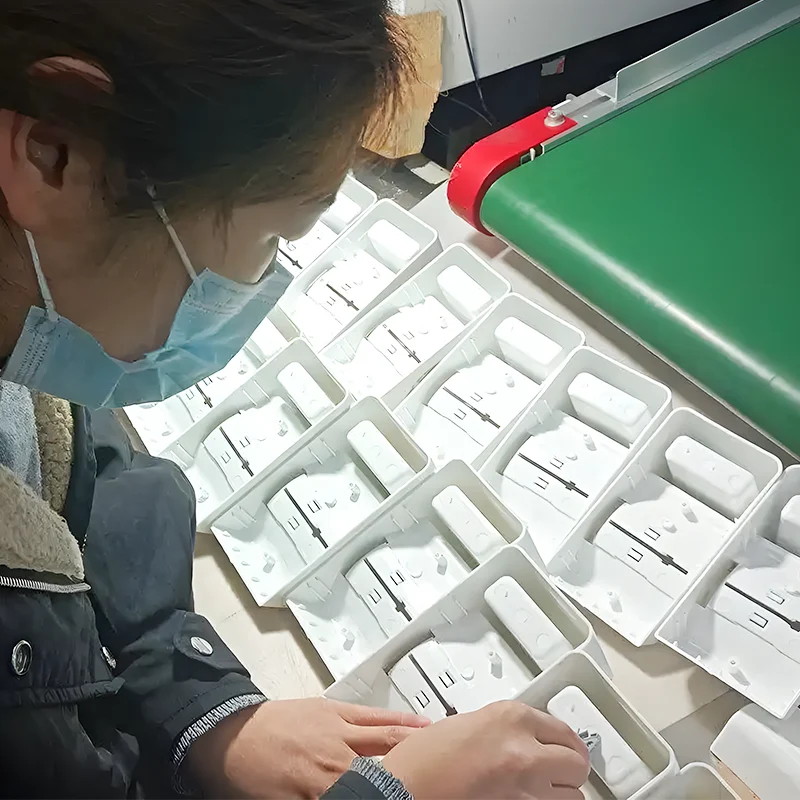
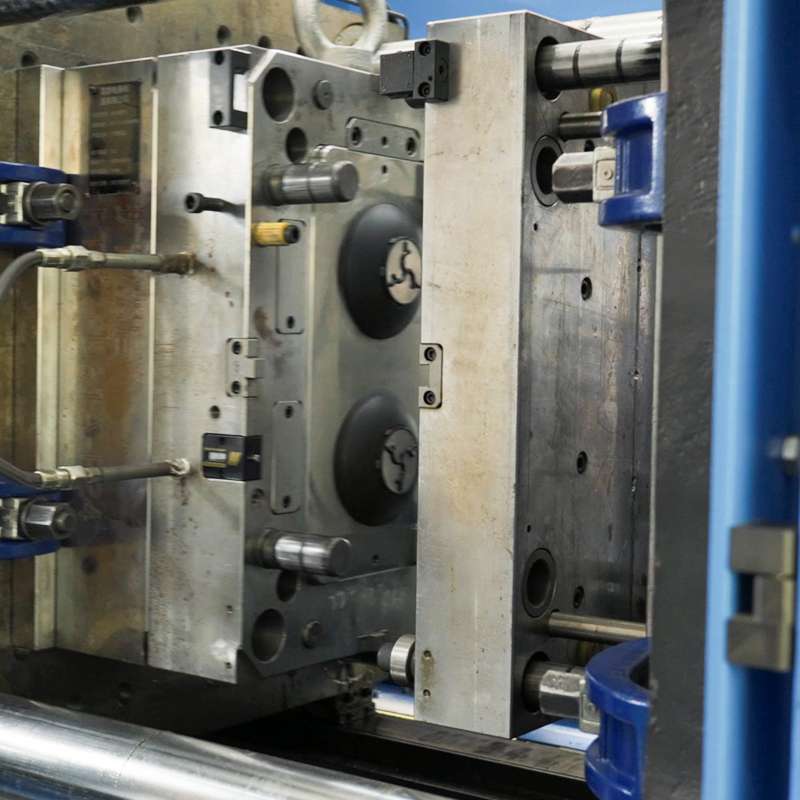
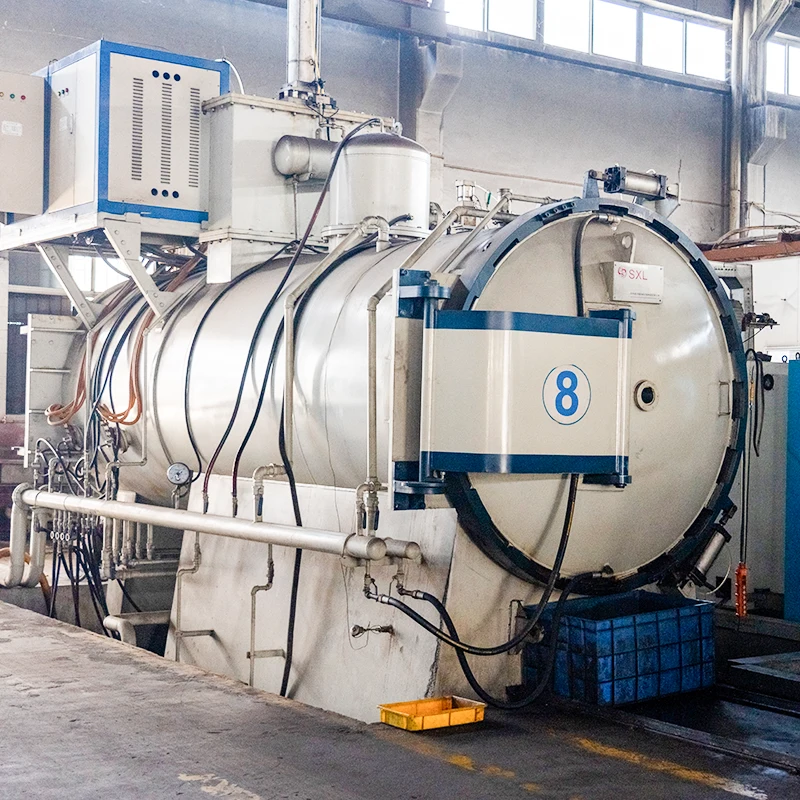
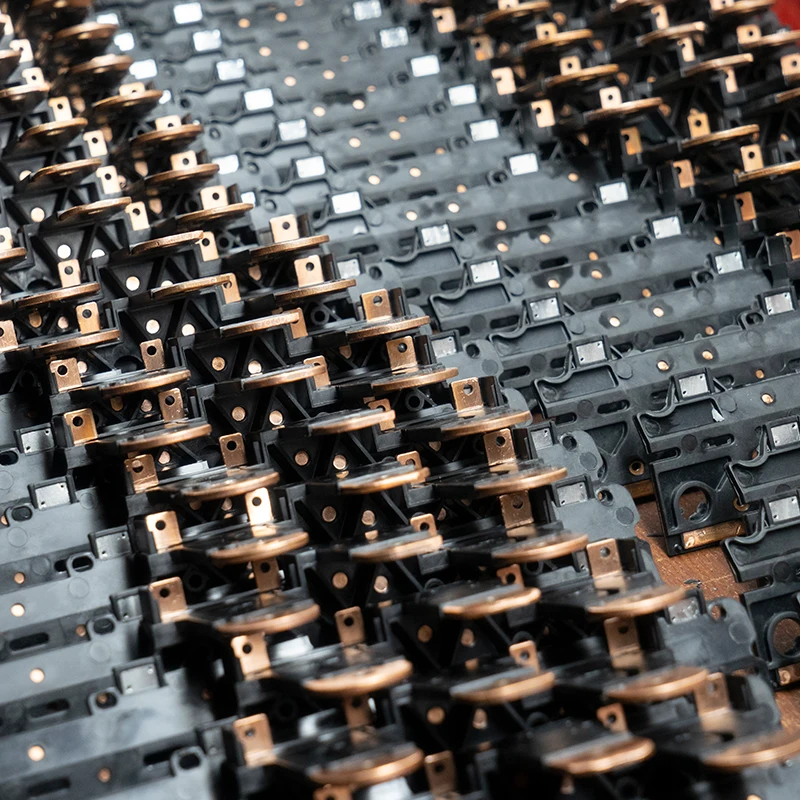
Appliances are found and form an integral part of everyday lives. We rely on them for several functions, such as cooking, personal grooming, entertainment, and other essential applications.Appliance injection molding creates plastic parts for several appliances, including refrigerators, stoves, washing machines, and microwaves. With the evolving technology, the need for energy-efficient appliances is transforming injection molding to satisfy consumers changing demands.
Home appliances have revolutionized how we live by extending convenience into every area of our lives. Plastics have made them affordable, longer-lasting, and more versatile. They rely heavily on injection-molded components for their functionality and aesthetic appeal. Manufacturers can order custom parts based on the unique needs of the project as assigned by the consumer. For instance, some appliances may benefit from specific resistances, whether to heat, chemicals, corrosion, or more, while providing reliable performance.
As consumer preferences continue to change to more sustainable and efficient products, the durability and precision of our products cannot be downplayed. Industries are focused on lowering production costs and increasing the longevity and efficiency of their products. Leveraging the benefits of Injection molding, it offers a solution by making it a cornerstone of modern appliance manufacturing.
What Appliances Use Injection Molding Processes?
Refrigerator Components
They like sliding drawer frames and in-door shelf units that store condiments and jars likely use injection molding. Fridge, freezer door handles, and many components used in ice makers, like the plastic auger dispensing ice on demand, are derived from a mold.
Dishwasher Components
Much of the interior of modern dishwashers comes from injection molds, such as the door or hatch leading to the detergent dispenser, the dishwasher racks themselves, the silverware caddies, and the water-spraying wash arms.
Keukenapparatuur
Common kitchen appliances like coffee makers,blenders,microwave ovens, and toasters use injection-molded parts extensively. Plastic food storage containers also use molding.

Washing Machines and Dryers
Washing machines contain many injection-molded components, including detergent dispensers, control knobs, and outside casings. These parts must be robust and water-resistant to withstand the high temperatures and high moisture levels inside these appliances.
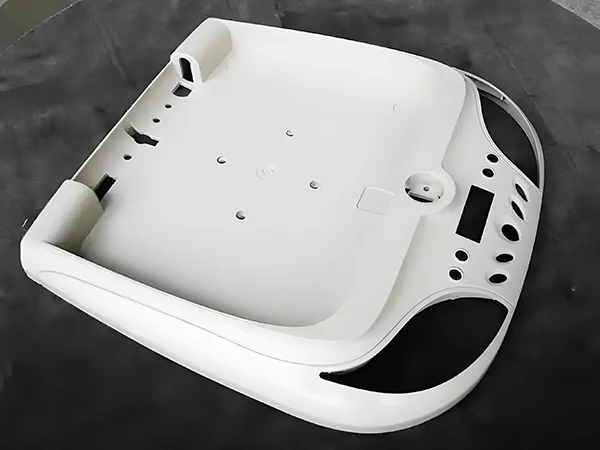

Air Conditioners
Grills, fan blades, and housing units are among the precise, superior plastic parts needed in air conditioners. Through injection molding, producers may create components with complex geometries, high heat resistance, and adequate ventilation and cooling.
Vacuum Cleaners
Injection-molded plastic components are used in vacuum cleaners for practical and aesthetic reasons. This process builds the appliances’ handles, casings, wheels, and hose attachments, which makes them lightweight but strong enough to handle frequent usage.
Small Electrical Appliances
Devices like electric kettles, irons, and hair dryers rely on injection-molded plastic parts. These components are usually the wiring enclosures, buttons, and outer casings; they must all be sturdy, heat-resistant, and electrically safe.
Television and Entertainment Systems
Injection molding is utilized in the consumer electronics industry to create speaker grills, remote control housings, and television casings. These components must have precise design while retaining durability and aesthetic appearance.
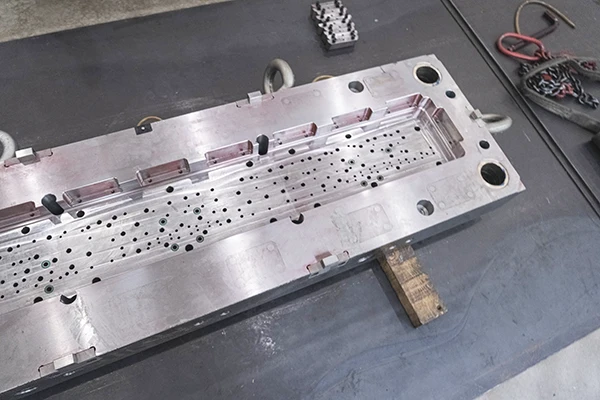
Smart Home Devices
Because of the development of smart home technology, injection-molded components are now more frequently seen in gadgets like security systems, home assistants, and smart thermostats. These gadgets must be heat resistant, have streamlined designs, and secure small electronic components.
Types of Injection Molding Techniques for Home Appliances
The manufacturing process requires employing various techniques to produce desirable outcomes.
Thermoplastic Injection Molding
This is the most widely used technique for creating plastic parts for home appliances. It is a cornerstone of modern appliance manufacturing, offering a versatile and efficient method for producing a wide range of plastic components. Thermoplastic materials like polycarbonate(PC), polypropylene (PP), and ABS are molded into essential appliance components, such as casings, knobs, and interior frames. Thermoplastic injection molding produces the outer casings and interior components of appliances like refrigerators, ovens, and washing machines.
Tussenvoegsel Vormen
It involves pre-manufactured materials, such as metal inserts or other non-plastic elements, being inserted into the mold during insert molding before the plastic is injected. The mold will form around the insert, resulting in a strong bond.
Typical applications in appliances that require durable connections. Including smart home devices, screws and fasteners in vacuum cleaners and air conditioners, oven doors, etc.
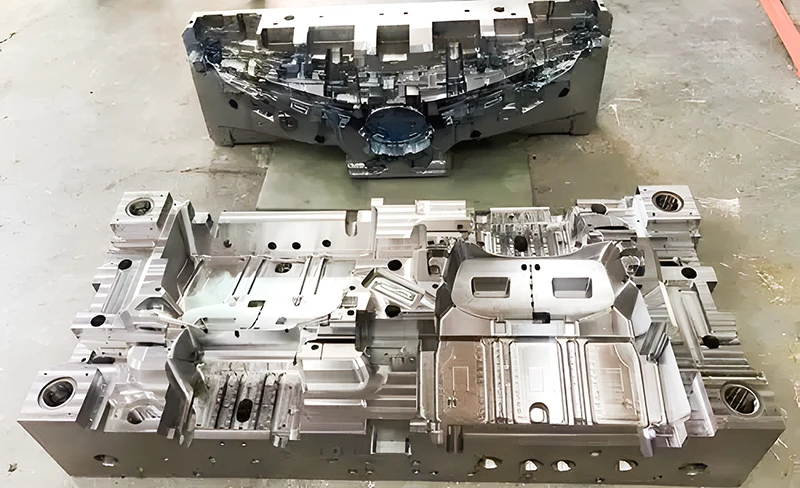
Gas-Assisted and Water-Assisted Injection Molding
Gas-assisted and water-assisted injection involves the simultaneous introduction of the plastic melting into the mold cavity using pressurized gas or superheated water. Due to the versatility of these techniques, they have become popular in producing various injection-molded products process. The plastic melt encases the gas or water, leading to a layered structure in the molded product. Solidification occurs when gas and water are released to allow demolding. Products created through this technique exhibit minimal shrinkage, material efficiency, and good rigidity.
A prime example of their application is creating television casings and air conditioner panels.
Schuim Spuitgieten
During this process, the manufacturer injects a foaming agent with the plastic resin into the mold cavity. The plastic cools and solidifies, expanding the foaming agent and creating a part with a foam core. This method decreases the part’s density, preserving its strength but making it lighter. This method is suitable for appliances where weight reduction and rigidity are essential. Such components are Sound-dampening components in dishwashers and insulating components in the oven and microwaves.
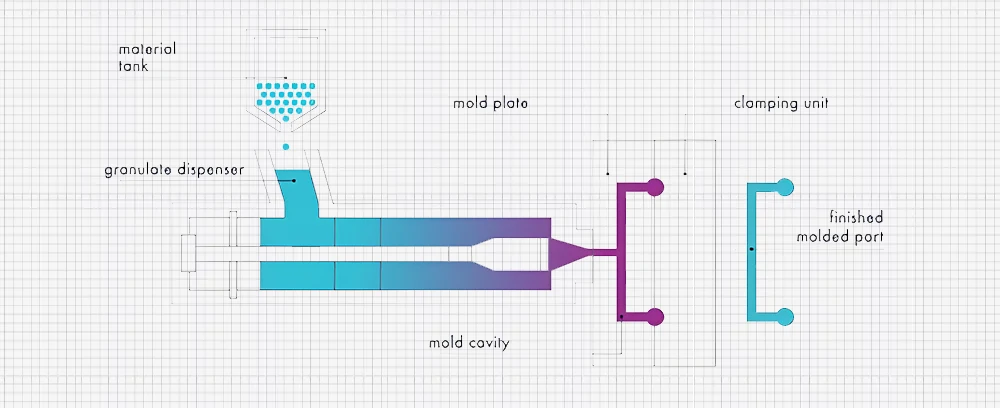
Fusible Core Injection Molding
Fusible Core Injection Molding (FCIM) is an advanced technique for creating complex hollow or internal geometries. This procedure inserts a fusible core into the mold, such as a metal or alloy with a low melting point. The plastic is then injected around the core. A hollow or finely structured internal structure remains when the part is created and the core is melted and removed.
This technique is highly beneficial for creating parts with intricate internal cavities, undercuts, or channels. Such appliances are dishwasher spray arms, vacuum cleaner nozzles, and coffee machine components.
The Role of Design in Appliance Injection Molding
Product design is the fundamental principle of appliance injection molding’s success. It directly influences the overall product’s durability, functionality, and appearance. The design process must incorporate the product’s molding method’s technical capabilities and performance requirements.
Mold and Part Design
The design phase is important in ensuring the process runs seamlessly and efficiently. The designer must consider the part and mold geometry, wall thicknesses, draft angles, and material selection. These elements impact how the molten plastics fill the mold and cool off, affecting the part’s structural integrity. A well-thought-out design reduces secondary operations conversely while minimizing production costs.
Collaboration Between Designers and Engineers
For successful appliance injection molding, a collaboration between product designers and injection molding engineers must be established. Designers concentrate on creating efficient and visually appealing parts, while engineers ensure these designs can be made using injection molding. Through collaboration, designers might propose changes in the ergonomic shape of a component, while engineers will adjust the design, including material distribution.
Innovative Designs Through Injection Molding
The precision and flexibility of injection molding enable innovative designs that conventional manufacturing cannot easily attain. For instance, using the over-molding process to create multi-material parts enhances functionality and comfort.
Thin-wall molding technology facilitates the creation of lightweight yet strong parts vital to modern design.
Parts with intricate internal geometries would be challenging to manufacture using other methods. Those with in-built snap-fit joints reduce the need for adhesives and screws during assembly.
Materiaalkeuze
During the design process, the material of the chosen plastics must be considered. Material moldability is also a crucial factor. Appliances used daily and expected to last for years must use durable materials for more extended service. The type of material also affects the appearance of the appliances. Different materials exhibit distinct textures and finishes, which allows the designers to achieve the desired output.
Kwaliteitscontrole
The quality of appliance injection molding is an essential approach to consider when designing and producing parts. Manufacturers rely on different procedures to maintain consistent component performance, minimize errors, and enhance part quality. Tolerance analysis and Design for Manufacturability (DFM) are critical for early-stage quality control, ensuring problems are addressed before full-scale production.
DFM focuses on optimizing part designs for ease of manufacturing. Incorporating DFM principles in the early stages of product development can assist manufacturers in detecting and addressing possible production issues before full-scale production starts.
Tolerance analysis ensures parts meet the precise specifications. Even tiny variations in the appliance’s size, shape, or fit can impact its functionality.
Therefore, strict tolerances required for injection molding are non-negotiable.
The Advantages of Injection Molding for Appliances
1. One of the biggest benefits of this approach is that it allows for making highly detailed shapes and complex designs with remarkable accuracy. High-pressure injections allow molten plastics to reach into the deepest, smallest parts.
2. High-volume production of products to meet the high demand with minimal lead time at low cost. The initial mold can be used repeatedly for long production runs, enhancing the production of similar products.
3. This repeatability ensures that every part of the assembly fits perfectly per requirements. It also minimizes waste and reduces defects.
4. Large volumes of production result in exceptionally cheap production costs per unit, even if the initial expenditure in designing and fabricating an injection mold may be substantial. Injection molding is the most preferred choice for major appliances.
5. Depending on the appliance’s needs, producers can select from a wide range of plastics using injection molding, including thermoplastics, elastomers, and even biodegradable materials. Additionally, producers can add fillers to improve the materials’ properties.
6. Advanced processes like over-molding and insert molding offer a significant advantage in producing different appliances. Components can be created with multiple materials and textures through over-molding, and non-plastic components can be incorporated to enhance functionality and durability in insert molding.
7. Many injection molding systems can recycle excess materials and utilize advanced technologies to reduce energy consumption. This has improved in terms of efficiency and waste reduction.
8. Injection molds with finished surfaces offer precision to the molded parts. This reduces the need for secondary operations like painting, trimming, or machining. It also reduces the cost of labor and saves time, which ensures the parts are ready for assembly.
The Future of Appliance Injection Molding
Several emerging technologies and market trends shape how manufacturers approach plastic design and production. These advancements assist the appliance industry in meeting growing consumer demands for high-performance, eco-friendly products.
Technological Advancements in Appliance Injection Molding
Among the emerging technologies that are set to revolutionize injection molding processes are:
- Automation and Robotics: Automation plays an important role, particularly for high-volume production in the appliance sector. Robotic machines can speed up production while reducing human error by handling tasks like part inspection, assembly, and mold loading and unloading. These devices are beneficial for manufacturing intricate appliance parts.
- Industry 4.0 and Smart Manufacturing: Integrating smart manufacturing devices like machine learning algorithms, the Internet of Things (IoT) and advanced sensors allow for better control over the injection molding process. Smart factories will become more common, allowing manufacturers to attain higher operational flexibility and efficiency levels.
- 3D Printing for Rapid Prototyping and Tooling: Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, allows designers and engineers to create plastic product prototypes quickly. This cuts the lead times and facilitates quicker iterations of the product.
Industry Trends and Predictions For Growth
Significant changes are occurring in the appliance injection molding sector due to the global market dynamic.
- Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Manufacturing: Appliances with recycled materials and energy-efficient designs are in high demand as consumers are concerned about the things they buy effects on environmental growth. In response, producers of injection molding are implementing greener techniques by employing recycled or biodegradable polymers and maximizing material efficiency.
- Customization and Personalization: The appliance industry is impacted by consumers’ desire for personalized and customizable items. This desire influences products by changing the textures, colors, and finishes.
- Global Supply Chain Shifts: Geopolitical factors, such as trade disputes and the COVID-19 pandemic, have forced corporations to reconsider their international supply chains. Reshoring or near-shoring is a popular strategy companies use to lower risks and lessen reliance on foreign suppliers.