For product developers, Design for Manufacturing (DFM) isn’t likely unfamiliar. If you’ve dealt with mold or injection factories, you’ve probably received DFM reports detailing your product’s essential information, key points, gating positions, and thickness analysis.
Indeed, you might have heard of this term even before engaging with injection factories. It’s a concept focusing on the manufacturability of products, applicable across various industries like automotive, electronics, aerospace, medical devices, and consumer goods.
Today, we’re delving into DFM for plastic products, aiming to provide you with a comprehensive understanding.

What Is DFM For Plastic Products?
DFM, or Design for Manufacturability/Manufacturing, entails considering manufacturability and assembly factors from the outset of design. Its role includes analyzing design information for process feasibility, evaluating manufacturing feasibility, and providing design improvement suggestions, all aimed at achieving the lowest cost, shortest time, and highest quality in production.
Traditional DFM Analysis Process For Plastic Products:
DFM’s role in the entire product development process is depicted in the diagram below:

In companies with both product development and injection production departments, the traditional process involves DFM report creation after product design completion but before mold development.
The report covers mold and molding aspects, such as shrinkage, mold steel, 注塑材料, gating positions, wall thickness analysis, 分线, and more.
Some companies provide detailed reports, including surface finish requirements, draft angles, insert lines and ejection positions. Moldflow analysis might also be incorporated, predicting optimal gate positions, sink marks, weld lines, gas trap risks, and improvement suggestions. After the report’s completion, it’s submitted to the product development department.
Engineers adjust product structures iteratively to meet mold design, and processing requirements, and minimize injection molding costs. Companies solely dedicated to product development hand over DFM reports to product manufacturing firms. This traditional approach persists in over 98% of product development processes in the market.
Advantages Of Plastic Products DFM
With DFM reports, product development engineers can conduct real-time analyses, offering several advantages:
1. Minimizing later manufacturing issues assessment gaps, preventing defects, elongated development cycles, and increased costs.
2. Streamlining the development process, enhancing engineers’ and teams’ efficiency, reducing development time and costs.
3. Facilitating real-time product design modifications for optimal designs, high-quality products, improved manufacturing efficiency, and reduced production and development costs.
4. Further synchronous mold flow analysis provides a genuine preview of the injection molding process, effectively evaluating production equipment needs, processing parameters, and guiding mold design.
5. Cost-benefit analysis through DFM optimizes product design, reducing mold, material, and production costs, and enhancing competitiveness in the market.
6. Material impact analysis ensures selected materials meet environmental standards, contributing to an eco-friendly society without pollution.
How To Make A DFM Report?
The DFM report directly reflects the designer’s level of expertise and proficiency, as it determines the mold’s quality and cost while showcasing the mold company’s technical prowess. In the following section, I’m going to provide an example of a relatively straightforward report to illustrate its structure and components.
To begin with, creating a DFM report necessitates utilizing software such as UG, screenshot tools, and PPT software. UG software, being a professional tool, requires specialized training to use effectively; Meanwhile, screenshot and PPT software are relatively straightforward and commonly available on most computers. If you’re unfamiliar with these tools, abundant online resources can assist you in acquiring the necessary knowledge.
The subsequent sections outline the key components typically included in a simple DFM report:
Table of contents of the Design for Manufacturing (DFM) report
The DFM report’s table of contents, similar to a book’s table of contents, provides a comprehensive overview of the report’s content.
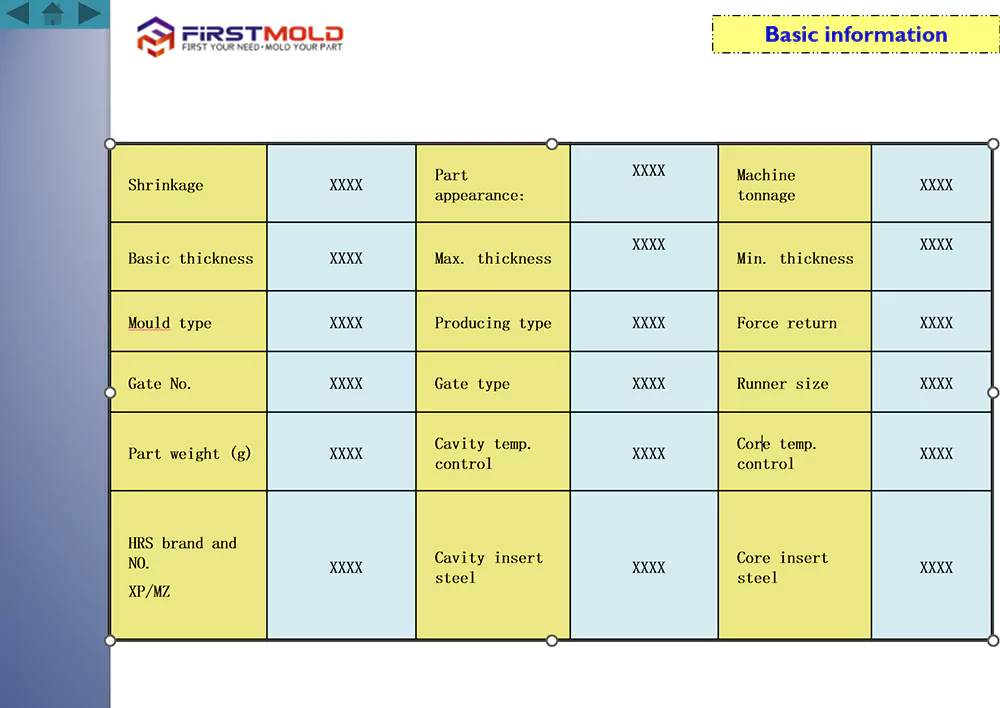
Basic Information
This basic form aims to gather crucial information about the product and injection mold, including details on plastic material, process conditions, and mold number. These details are of utmost importance and must be accurately confirmed with the customer, leaving no room for errors. Customers themselves often provide this information in many cases.

Product Craftsmanship Requirements
This section primarily focuses on capturing the customer’s requirements regarding the product size, surface specifications, and other related aspects. By documenting these requirements, we ensure that the design process accurately incorporates the appropriate insert sizes, orderly placement of inserts and ejector pins, and other relevant considerations. When specific surface requirements are involved, such as raised areas, it is crucial to provide the customer with a visual representation or color sample for their confirmation and approval. This helps guarantee that the desired surface specifications are met with precision.

Injection method and position
This page primarily presents crucial mold design details, including the placement of the product’s gate entry point and the size of the runner. It addresses important considerations such as determining the appropriate gate type, whether to use a hot runner or cold runner system and specifying the type and brand of the hot runner gate. All of these elements require a confirmation from the customer to ensure accuracy and prevent potential design errors down the line.

Draft Angles Analysis
This section assesses the product’s core and cavity draft angles’ adequacy. It’s crucial to determine whether the draft angle is sufficient, particularly when the product surface requires textures, plating, or other special treatments.

Parting Line Confirmation
This section primarily addresses the positioning of the product’s parting line and clip line, ensuring their proper placement and assessing the overall reasonability of the parting. By carefully determining the optimal parting line and clip line positions, we aim to achieve a well-designed and efficient mold that meets the requirements of the product.

Ejector Position confirmation
This section focuses on the ejector pin method and the positioning of ejector pins for the product. It involves determining the appropriate ejector pin design and placement to ensure smooth ejection of the product from the mold. By meticulously considering the ejector pin method and position, we can optimize the ejection process and minimize the potential for product or mold damage.

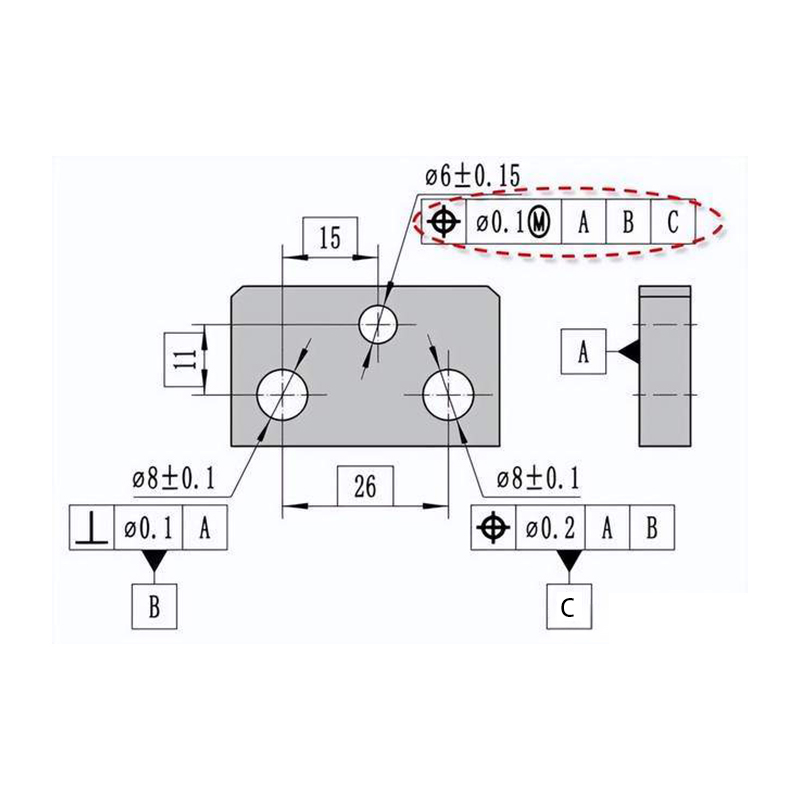
Wall Thickness confirmation
Wall thickness analysis is a crucial step in the DFM process as it helps evaluate the uniformity of the product’s material thickness and identify potential issues such as 沉痕 on the surface. Typically, areas highlighted in red indicate regions prone to shrinkage. Based on the analysis, we can provide recommendations to customers, such as reducing material usage or modifying the product design to address these concerns. By optimizing the wall thickness, we can enhance the overall quality and performance of the molded product.

Product problem analysis and solutions
This section holds significant importance as it allows us to identify and address potential issues, serving as a key indicator of a mold designer’s expertise in conducting a DFM report. Conversely, fewer product problems signify a more advanced level of product development, where mold designers may struggle to uncover any issues. This aspect serves as a crucial measure of the competence of product development personnel. By thoroughly analyzing and resolving these problems, we can enhance the overall quality of the product and streamline the mold design process.

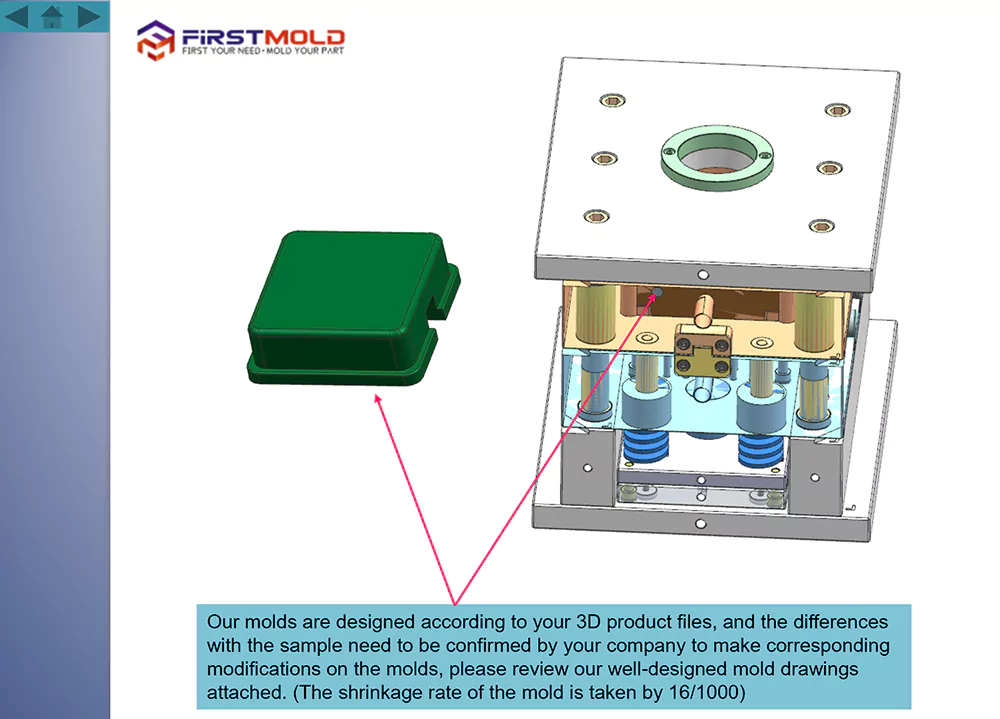
Others
We employ mold flow analysis for products with intricate customer requirements as a part of our DFM reporting process. The mold flow analysis report comprehensively evaluates various factors that need to be confirmed with the customer. These include filling time analysis, air trap analysis, weld line analysis, system pressure, and more. By conducting a thorough mold flow analysis, we can ensure that the design meets the customer’s specifications and identify any potential issues early on, allowing for necessary adjustments.

A Controversial Topic On DFM For Plastic Products
Plastic product DFM reports should be handled by the product designers of the product development company or by the mold designers of the injection molding factories and other manufacturers?
Currently, it seems that the mainstream view is that DFM should be handled by mold designers rather than product designers. The reasons are as follows:
1. not every designer is highly proficient in molds and injection molding;
2. specialization is key, and professional matters should be entrusted to professionals.
Some new viewpoints argue that DFM is a team effort, primarily the responsibility of product design engineers, followed by manufacturers. There are mainly three reasons:
1. It helps reduce costs to minimize expenses:
From the perspective of product cost, manufacturers and product designers have different positions, sometimes even conflicting.
Manufacturers are primarily concerned with how much profit they can make from producing the product, and secondly, whether the product can be produced smoothly. From the manufacturer’s perspective, higher product costs naturally lead to higher profits for them.
However, for product design, the focus is on minimizing product costs while still ensuring smooth production.
From the perspective of some manufacturers, they have no incentive to actively inform designers of cost-saving measures during DFM.
2. Shortening the product development cycle.
Secondly, only when product design engineers are responsible for DFM can repetitive design modifications be avoided, thus shortening the product development cycle.
If manufacturers handle DFM, when do they start? Usually, manufacturers start DFM after the detailed product design is completed and when the product is ready for mold manufacturing, upon the client’s request.
Clearly, doing DFM at this stage is too late. If DFM wasn’t considered from the start of product design, there will be many areas in the manufacturer’s DFM report that require design modifications. At this point, the product design is already finalized, and making modifications would be time-consuming and labor-intensive. Even a small modification may involve changes to multiple components.
This not only increases the workload of designers but also reflects poorly on their professional competence. Why not consider DFM during product design? Considering DFM during product design, rather than solely relying on manufacturers, would significantly reduce repetitive design modifications, thus shortening the product development cycle.
3. Manufacturer-led DFM cannot replace design perspective DFM.
Supplier-led DFM reports purely view design from a production perspective. Design perspective DFM should include more aspects, such as wall thickness design, enhancing part strength, and aesthetics.
Therefore, supplier DFM reports cannot replace design perspective DFM. Otherwise, optimization opportunities in terms of product appearance, strength, and cost would be missed.
What are your thoughts on these two different viewpoints?
FirstMold’s Viewpoint:
In our opinion, DFM is not simply a technical aspect; in a sense, it is more like a mindset embedded in various stages of product realization. Narrowly speaking, it involves considering production conditions for manufacturability. Broadly speaking, design should meet diverse production requirements, offering more choices and cost reduction. It’s about Design for Money – creating value through design!
It’s undeniable that manufacturers provide DFM, but this process must always involve timely feedback to clients and convincing them with a customer-oriented approach to achieve mutual benefits. For product designers, being able to grasp DFM techniques is undoubtedly beneficial. It not only leads to better product designs but also greatly enhances one’s own capabilities.
结论
As mentioned earlier, the DFM report analyzes the product from two main perspectives: the product side and the tooling side. This comprehensive report provides a deeper understanding of the product and requires technical expertise to ensure accuracy. It is intended to provide valuable insights and assistance in the design process.
Once the DFM report is completed, the next crucial step is to engage in detailed discussions with the customer. Each item in the report is reviewed and confirmed with the customer to ensure alignment. Only after this thorough review process is completed the mold designer can proceed with designing the mold based on the agreed specifications.