Parasolid file format is native to the Parasolid geometrical kernel, a widely used 3D geometric modeling kernel in the computer-aided design (CAD) industry. Parasolid is widely used as a geometric kernel or interoperability format in PLM software like NX and SolidEdge. It provides a flexible and powerful system for modeling and handling 3D geometric data.
Parasolid has 900+ features and provides various modeling techniques, such as solid modeling, free-form surface, and direct editing. Parasolid displays extensive graphics and rendering capabilities, including accurate wireframe and hidden line drawings. It offers convergent modeling technology, which enables models based on facet representations to benefit from its reliable B-rep modeling functions.
Additionally, it offers flexible tessellation options and a comprehensive set of model data queries. Many CAD software use Parasolid files for interoperability so that the 3D model can be accessed.
A brief history of Parasolid file
Siemens Digital Industries Software, a renowned leader in CAD/CAM/CAE technologies, established the parasolid file format. Siemens designed Parasolid as a core 3D modeling kernel, aiming to integrate it into CAD software. This would allow designers and engineers to develop accurate and detailed 3D models. Many industries embraced Parasolid as a standard and blended it into popular CAD software like SolidWorks, Siemens NX, and Autodesk. Siemens aims to ensure Parasolid remains a leading geometric modeling technology through constant development.
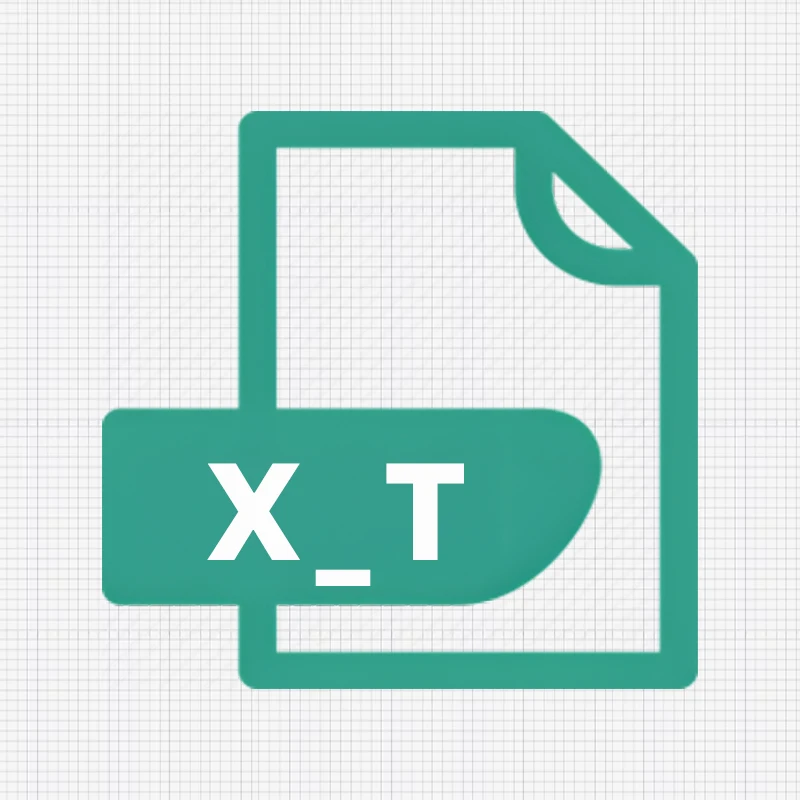
X_T and X_B File Types
Parasolid has two primary file extensions: x_t denoted as Parasolid Text Transmittal, a text-based format, and. x_b as Parasolid Binary – binary-based format. The .x_t extension files are usually used in Solidworks as they contain more information about the 3D model. In case of any error, while working with .x_t files, the .x_b file type is also used. It helps create a solid model from a part file as a separate file.
(i)The X_T File Format
The X_T file format, a text-based file format, stores 3D geometry models, especially those created using CAD (Computer–Aided Design). X_T files are part of the Parasolid family and are used in product design, simulation, and production. They feature precise illustrations of the geometry and topology of 3D objects, such as surfaces, edges, and solid bodies. The main objective of the X_T format is to offer a readable and portable way for design teams or various software systems to share 3D models. This nature allows manual inspection and modification, which can assist with special design elements or troubleshooting.
Structure and Components of an X_T File
- Header- includes the metadata like the file version, information about the software used, and the Parasolid Kernel version. This section ensures compatibility during the exchange of files among various CAD systems.
- Geometry Data: the central region of the x_t file that holds geometric information describing the 3D model.
Elements found within include:
- Vertices: coordinates defining significant locations in space.
- Edges: Vertex lines that establish the bounds of the model.
- Faces: Surface information that characterizes the object’s exterior.
- Solids: describes volumetric entities, like solid bodies.
- Topological Data: the information about how different elements relate. This data is necessary to develop a coherent and complete 3D model.
X_T file can be easily viewed and edited through a text editor. Manual modification, on the contrary, can be difficult, so it’s only done for troubleshooting or specific adjustments.
(ii)The X_B File Format
This binary-based file format acts as a storage space for 3D geometric models. Similarly, they are a part of the Parasolid family and are extensively applicable to CAD, CAM, and CAE applications. X_B files hold data in a binary format, making them more compact and quick to process. This distinguishes it from the X_T files, making it the main objective of the format.
Improving the performance when handling complex assemblies and large models makes it ideal for many large-scale applications.
Structure and Components of an X_B File
- Binary-Encoded Header: much like x_t files, x_b files begin with a header containing metadata regarding the file version, software used to create the file, and the Parasolid version. However, the data is stored in a binary format to save space.
- Binary Geometry Data: similarly, X_B files store 3D geometric data in binary form, which includes Edges, Vertices, Faces, and solids.
- Topological Data: the file shows the topological relationships between data stored compactly to save space.
Both file formats exhibit the same data. However, the binary format is a little more compact and is easily processed faster by the software. The Parasolid file format is proprietary, developed by Siemens, and widely used in CAD systems that support the Parasolid kernel. The main benefit of the Parasolid file is that it remains the same as the actual 3D model.
Creation and Exporting of Parasolid Files
Creating Parasolid files is rather straightforward for the CAD software, which supports the Parasolid kernel. With a few minor menu layout differences, exporting Parasolid files as X_T or X_B formats is a similar process for all CAD platforms. Here are some steps of some of the popular CAD software used:
Solid works
Creation of a Parasolid File: after completing your 3D model in Solidworks, Parasolid files are created as an export option. To ensure compatibility with Parasolid formats, SolidWorks uses Parasolid as its native geometric modeling kernel.
Steps:
- Open your part or assembly in SolidWorks.
- Go to File → Save As.
- Set the “Save as type” dropdown menu, and choose Parasolid (*.x_t) o Parasolid Binary (*.x_b).
- Select the location to save your file and click Save.
Siemens NX
Creating a Parasolid File, creating X_T and X_B files is a breeze, Since Siemens NX is found to have a built-in modeling engine called Parasolid.
Steps:
- Open your part or assembly in Siemens NX.
- Navigate to File → Export
- Choose Parasolid.
- Specify whether you want to export the file as X_T o X_B file.
- Choose your preferred location to save your file, then click OK.
Autodesk Inventor
Creation of Parasolid File: Autodesk Inventor does not have built-in support for Parasolid. Users can export their files in Parasolid formats to ensure compatibility with other CAD programs.
Steps:
- Open your part or assembly in Autodesk Inventor.
- Select File → Export
- Choose CAD Format.
- In the “Save as type” dropdown, select Parasolid (*.x_t, *.x_b).
- Select your preferred format (X_T or X_B) and click Save.
Comparison with Other File Formats
Parasolid has excellent data translation capabilities. It can read and write file formats like STEP, IGESy STL, among other different formats.
However, it’s hard to comprehend how Parasolid files (X_T and X_B) differ from other well-known CAD file formats, such as IGES, STEP, and STL. In that case, there is a dire need to discuss them to get better insight and make good comparisons. Depending on the application, and industry requirements, each format has pros and cons that affect how they operate.
Comparison Table: Parasolid vs. IGES
| Parasolid (X_T/X_B) | IGES |
| Text-based (X_T) and Binary (X_B) | Text-based |
| File extension .x_t, .x_b | File extension .iges, .igs |
| Its purpose is to produce 3D solid and surface modeling and parametric modeling. | Purposed for Data exchange for 2D/3D CAD models |
| Supports Solid modeling, surface modeling (Boundary Rep/B-rep) | Primarily supports 2D and 3D surface modeling |
| Supports parametric and feature-based modeling | It does not support parametric data |
| Handles complex, highly detailed geometries | Struggles with complex, detailed 3D geometries |
| X_T files are human-readable; X_B files are not | Human-readable (text format) |
| Native to Parasolid-powered CAD systems (SolidWorks, Siemens NX) | Widely supported across many CAD systems |
| Faster performance due to binary option (X_B) | Slower due to larger file sizes and older technology |
| Fully supports Boolean operations on solids (union, subtract, intersect) | Limited support for Boolean operations |
| Common in industries requiring high precision (aerospace, automotive, manufacturing) | Supports older CAD systems or legacy data exchange in several applications. |
Comparison Table: Parasolid vs. STEP
Parasolid specializes in solid modeling within systems that support it. STEP is typically utilized for cross-platform data sharing, having excellent compatibility across various CAD software packages.
| Parasolid | STEP |
| File Extension .x_t, .x_b | File Extension .stp, .step |
| File Type Boundary representation (B-rep) | File Type Standardized data exchange format |
| Purposed for 3D solid modeling kernel | The main objective is to exchange data between CAD systems. |
| Data Structure is a B-rep solid model. | Data Structure B-rep, wireframe, surface, and PMI |
| Limited to Parasolid-compatible systems | Highly interoperable across CAD platforms |
| File Size Compact | File Size Larger, especially with metadata |
| Used for Design, analysis, manufacturing | Used for Data exchange, interoperability across systems |
Comparison Table: Parasolid vs. STL
This contrast illustrates how Parasolid leans towards detailed, parametric modeling in CAD applications, while STL is mainly used for Impresión en 3D and only represents the surface geometry without any extra information.
| Parasolid | STL |
| File Extension .x_t, .x_b | File Extension .stl |
| File Type Boundary representation (B-rep) | File type Mesh file format |
| Purposed for 3D solid modeling kernel | The primary goal is to 3D printing and CAD applications. |
| Data Structure B-rep solid model | Data Structure Mesh of triangular facets |
| Very high precision | Limited precision based on mesh density |
| Fully editable | Not editable post-export |
| Limited to Parasolid-compatible systems | Highly interoperable across CAD and 3D printing software |
| File Size Compact | File Size Can be larger for complex geometries. |
| Used for Design, analysis, manufacturing | Used for 3D printing, prototipado rápido |
Advantages and Limitations of Parasolid Files
Key Benefits of Parasolid Files
- Precisión:
Parasolid files can store very detailed and accurate 3D models. This ensures that the geometric information accurately represents real-world objects. This level of precision is good for large-scale industries like aerospace and automotive.
- Data Integrity:
By using boundary representation (B-rep), Parasolid files can keep track of the geometric and topological relationships between different parts of the model. This minimizes mistakes during design iterations by guaranteeing that any changes made to the model maintain its integrity.
- Compatibilidad
Parasolid is compatible with several CAD applications, especially those that use the Parasolid kernel (like SolidWorks and Siemens NX). This means that people using such software can easily share data and collaborate.
- Support for Advanced Modeling:
Parasolid can handle sophisticated operations like Boolean operations (combining, subtracting, or intersecting shapes), which is advantageous for complicated design tasks.
- Proper Handling of Large Models:
The binary format (X_B) offers a more compact representation of 3D models when compared to text-based formats, allowing for faster loading and processing of large assemblies. This means they are loaded and processed more quickly, especially for large groups of objects.
Limitations of Parasolid Files
1. File Size:
Parasolid files can still be larger than other interchange formats like IGES or STEP, even if the binary format minimizes file sizes compared to text formats. This can mean Longer file transfer delays may result while exchanging files.
2. Proprietary Nature:
Parasolid, a proprietary format developed by Siemens, can restrict its accessibility. This may lead to compatibility problems when sharing files with CAD software that doesn’t fully support the Parasolid format.
3. Learning Curve:
Users with minimal or no familiarity with Parasolid or particular CAD systems that adopt it may encounter a learning curve while figuring out how to take full advantage of its capabilities and file management system.
4. Limited Text-Based Option:
Although X_T files are edited or inspected manually, they are not as user-friendly as other formats despite being human-readable. The binary format (X_B) is completely unreadable, which makes troubleshooting more challenging.
Applications of Parasolid Files
Parasolid files are a cornerstone in computer-aided design (CAD) and have widespread application across various industries. These files assist in producing precise 3D models for design, analysis, and Finite Element Analysis (FEA) in many industries, including
- aerospace,
- automotive,
- manufacturing.
- Architecture and construction
- Medical device design…etc.
Conclusión
While Parasolid provides a robust foundation for CAD modeling, its proprietary nature presents a potential drawback. As the CAD landscape changes towards a growing focus on open standards and interoperability, it may pose challenges for proprietary formats like Parasolid. And the challenge must be dealt with. Strategies like licensing or open-sourcing parts of the Parasolid technology could foster wider adoption and compatibility, reducing the reliance on a single vendor. As the world continues to innovate, embracing tools like Parasolid can pave the way for breakthroughs in modeling and unlock new possibilities.