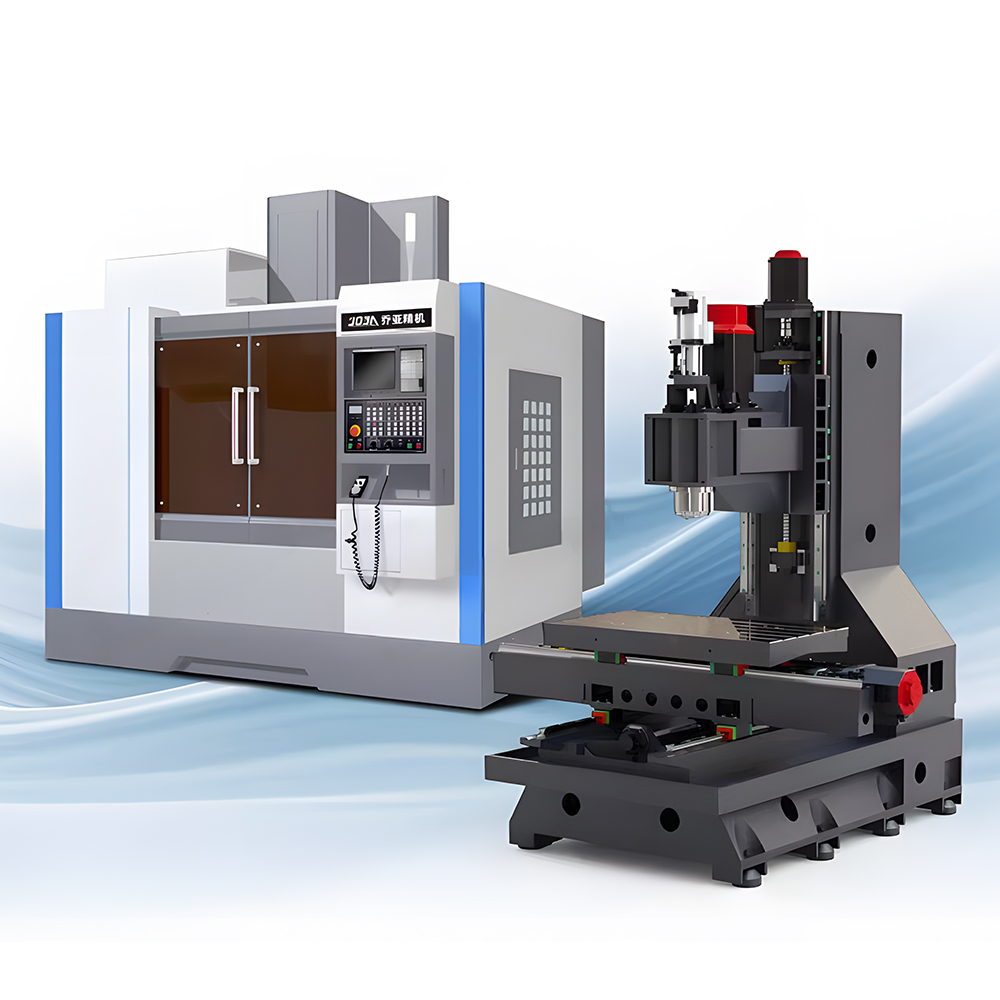
Milling machines, also known as mills, are rotary cutter-operated machines used to remove material from a workpiece. They are significant in the construction process, more particularly in the construction of parts with geometric dimensions. Milling machines are used in the automotive, aerospace, electrical electronics, and metalworking industries.
This article will highlight the features of using milling machines, different classifications, applications, and purposes of the milling equipment.

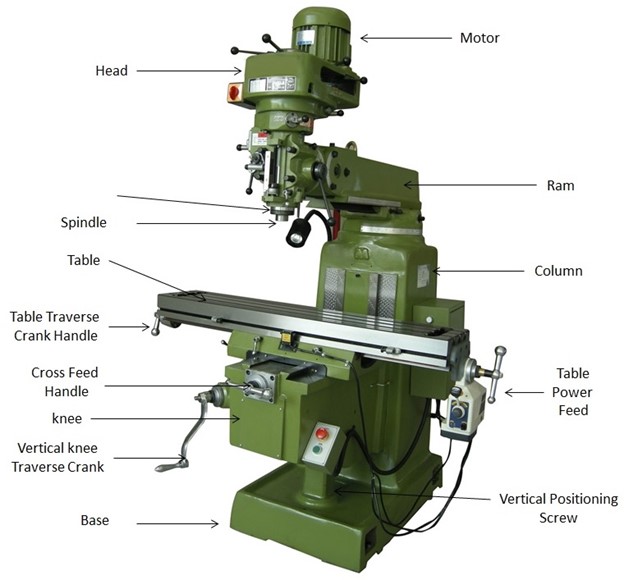
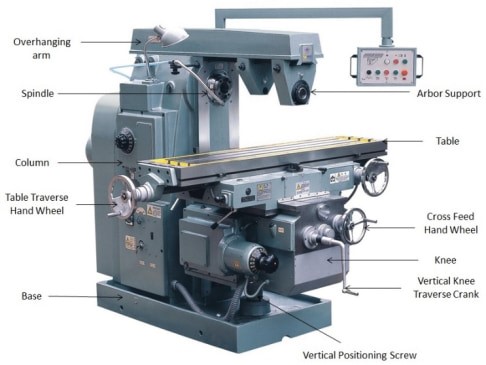
Structure and Parts of Milling Machines
The mills are complicated structures with parts that work harmoniously to execute several machining processes. Knowledge of these parts is essential to using them effectively and achieving maximum accuracy.
Base
A milling machine also has a base, which forms the core structure and safeguards the entire setup. Usually, the base is made of cast iron, which provides stability to the device during its operation and reduces the effect of shakes that can influence the accuracy of work.
Also, the base may incorporate the coolant reservoir since the coolant assists in cooling the cutting tools during milling to prevent heat build-up and subsequent effects on the cutting tools.
Column
On the base is mounted the column, which acts as the spine of the milling equipment and is composed of cast iron. It carries the spindle and motor and contains a drive system that governs the motion of the spindle.
Knee
The knee is connected to the column, an adjustable mechanism that supports both the saddle and the on-work table. It is designed to provide gliding vertical motion about the column that, in turn, enables fine control of the depth of the cuts; this is due to the presence of a vertical feed screw.
Saddle
The saddle is slid along the length of the knee in the Y direction while the knee slides along the length of the saddle in the X direction for precise positioning of the worktable with the workpiece.
Worktable
The worktable, which supports the workpiece during the machining process, is translated along the X and Y axes by the saddle and the knee. It comes with T-slots to support the workpiece and any other clamps that may be required during the work process.
Spindle
Adjacent to the worktable is the spindle, a central component of the mill, which holds and rotates the tool. According to the type of machine, the spindle could be either vertical or horizontal, with the feed rate controlled depending on the operation required.
Overarm, Arbor And Arbor
In horizontal milling machines, the overarm and arbor support the cutting tools, while in vertical milling, the quill guides the tool’s up-and-down movement.
These components are housed in the head of the machine, and the head may even sway for angular movements; the ram further enhances the positioning of the head about the workpiece.
Finally, the arbor is a cylindrical shaft used in horizontal mills. It holds the milling cutter and allows big, strong cutters suitable for brutal milling operations.
Types of Milling Machines
Milling machines come in various types, each tailored to perform specific tasks effectively:
Vertical Milling Machines
The vertical mills are established with the spindle’s movement in a vertical fashion along the Z-axis, while the cutting tool performs its operation on this axis. These designs make them suitable for plunge cutting, a process through which the tool goes straight into the material for holes or depressions.
Another advantage of vertical positioning of the spindle is the ability to drill appropriately, as a particular location of the tool over the workpiece is easily achievable. Vertical milling equipment are versatile and recommendable, especially in industries requiring high accuracy and precision in operations like shaping, cutting, and even drilling complex shaped parts, such as those in aerospace and automobile industries, among others.
The table can be moved along the X and the Y axis, which increases their flexibility since they can perform several operations without needing a change of position.
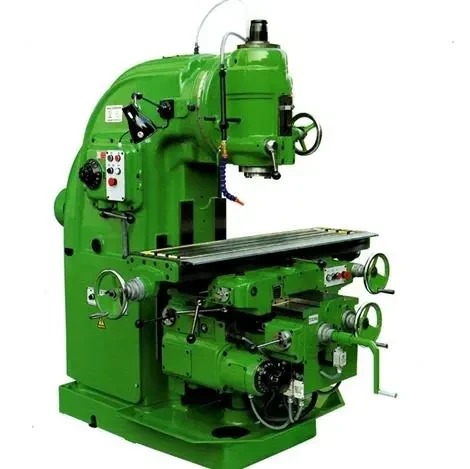

Horizontal Milling Machines
Horizontal Mills: Unlike vertical mills, the spindle of horizontal milling machines is placed horizontally and parallel to the work table. Therefore, it is suitable for slotting, grooving, and planning flat surfaces. This arrangement provides enhanced rigidity on the planar nature, which is beneficial for handling large and thick materials and performing challenging operations.
It is applied in operations that entail roughing processes, like cutting a large slot or making a wide groove in one pass. Their design is also suitable for using multiple cutting tools concurrently; this increases productivity rates since more operations can be performed in the first cutting cycle.
These machines are commonly used in manufacturing plants such as the heavy machinery, automobile, and metalworking industries since they provide high speeds and horizontal milling that are essential in developing large parts with the highest precision.

Фрезерные станки с ЧПУ
CNC mills are computerized controlled machines used to fabricate metals through the computer numerical control machining process whereby the computer programs the path to follow by the cutting tool. These automations make it very accurate and provide high precision, allowing the creation of fragile and complex components.
They are rigid and contain a high degree of tolerance for accuracy, especially for highly technical jobs requiring mathematical calculations and the ability to create products with identical dimensions. They are used in industries that deal with the production of many similar parts.
Because of the high accuracy of this equipment and versatility in handling tasks that are very time-consuming and sometimes impossible, CNC milling machines have become integral tools in industries such as aerospace, electronics, and health. With the help of different tool paths and operations, they can quickly change positions and be equally suitable for developing prototypes and serial production.

Universal Milling Machines
Universal mills are unique and effective tools combining vertical and horizontal milling machines. This makes it possible to mount the spindle vertically or horizontally to facilitate a wide range of operations, including boring, cutting, shaping, and slitting.
This flexibility of operation makes the universal milling machines most helpful where a variety of plain and profile milling operations are to be carried out, for instance, in toolrooms, repair shops, and workshops where output can be considerably increased by changing over from one type of milling work to another on the same machine.
These machines are suitable for various and more intricate operations given that the tables move in several directions in addition to the spindle movement; it can advance in the up position with powerful cutting and drilling capabilities that are characteristic of vertical mills or tilted horizontally to impact on the table surface with the same intensity provided by horizontal mills.

Bed Milling Machines
Bed mills have a fixed table and offer rigid support, which is best for heavy-duty milling operations. The table of a bed milling machine is stationary, and unlike other milling equipment in which the table runs on the X and Y axis, the spindle goes up and down on the Z axis.
This design greatly improves the structural stiffness and strength of the machine so it can handle large workpieces and perform operations that require force.
Bed milling machines are used in the automotive, aerospace, and construction industries, where there is a need to work on large and heavy parts. Due to the thicker metal cutting wings, cuts can be made deeper with high MRR, which makes the cutting tools ideal for applications such as roughing complex component structures, large mold machining, or manufacturing heavy-duty parts.

| Milling Machine Type | Max Spindle Speed (RPM) | Table Size (mm) | Max Workpiece Weight (kg) | Приложения |
| Vertical Milling Machine | 4,000 | 1000 x 500 | 500 | General machining, drilling |
| Horizontal Milling Machine | 3,500 | 1200 x 600 | 800 | Slotting, gear cutting |
| CNC Milling Machine | 10,000 | 800 x 400 | 300 | Precision components |
| Universal Milling Machine | 5,000 | 1100 x 550 | 600 | Complex part machining |
| Bed Milling Machine | 3,000 | 1400 x 700 | 1000 | Heavy-duty machiningdxcc |
Advantages of Mills in Manufacturing
Milling machines offer many benefits in manufacturing, which is why they are essential in different industries. The first of its kind is precision and accuracy since it removes the human element from the process, and what could be more impressive than that? Mills can also produce workpieces with high accuracy since they can work with high repeatability.
Whether it could be a small component or a large, complexly shaped part, the milling equipment ensure that every cut is precise, and thus, you find that every completed product from the milling machine is smooth. The subsequent products in the production batches are also smooth.
Another benefit of mills is that they are very flexible. They can work with many materials, including metals such as steel and titanium on one side and aluminum, plastics, and other composites on the other. This versatility enables manufacturers to use milling machines for various purposes, from producing engine parts and mold tools to medical equipment and electronic casing.
Due to the flexibility of the materials and operations during the milling process, mills are vital tools in manufacturing industries.
Another advantage is that it increases efficiency, especially when the milling is done using computerized Mills such as CNC. These are specialty machines used for milling and are preferred because they enhance the speed of the process, increase accuracy, and minimize errors that may arise from using human labor.
CNC milling machines can run 24/7 to create similar, more consistent parts for high-volume manufacturing. This improved efficiency also brings down the cost of manufacturing, hence making the milling equipment economical for manufacturers who wish to improve their efficiency.
Applications in Modern Manufacturing
Today, mills are needed wherever mechanical engineering is an essential branch of modern manufacturing processes. In the automotive industry context, milling machines are more critical when manufacturing engines and other significant components of automobiles.
Since milling machines are highly precise, complex parts, including engine blocks, cylinder heads, and transmission housings, can adequately be produced as they require high performance and reliability. These parties prove advantageous to the automobile industry. They provide versatility and the ability to accommodate small and large runs, which is crucial in vehicle manufacturing because they make it efficient and dependable.
Mills are common in aerospace industries for machining operations on parts with complicated cross-sectional geometries. The parts of aerospace structures are mainly small bulk and have intricate shapes and fixed dimensions because of the harsh working environment.
Mills are used in the machining of parts and components such as turbine blades, aircraft structural parts, and other structural members that require great accuracy and dependability. Substantial evidence validates that those parts meeting small tolerances and surface finishes guarantee reliable performance under high stress.
Primarily used in electronics manufacturing, specifically circuit boards and other forms of electronics sub-assembly. As a result, generating elaborate and precise patterns on circuit boards is essential for properly working electronic devices. Milling machines are extensively used to manufacture PCB substrates, make holes for mounting components, or etch fine circuits. This precision helps stabilize electrical products meant for domestic commercial and industrial purposes.
Заключение
Milling machines are among the most commonly used tools in manufacturing industries today because of their accuracy, flexibility, and their capacity to operate at high rpm in various operations. Beginning with the usual vertical milling that includes manual operations but is appropriate for precision, intricate work, and the modern computer numerical control milling that offers high-level automated control for complicated operations, these machines constitute an imperative part of many manufacturing industries.
Awareness of the strengths and versatility of the various mills enables the right tools to be taken to the manufacturers, therefore, precision, quality, or productivity. As part of manufacturing lines, milling machines enhance functionality, productivity, efficiency, and flexibility for licensees depending on the type of materials and designs required.
Due to their versatility and the precise drill they provide, these machines benefit any production environment and contribute to progress and sustained competitiveness in the production domain.