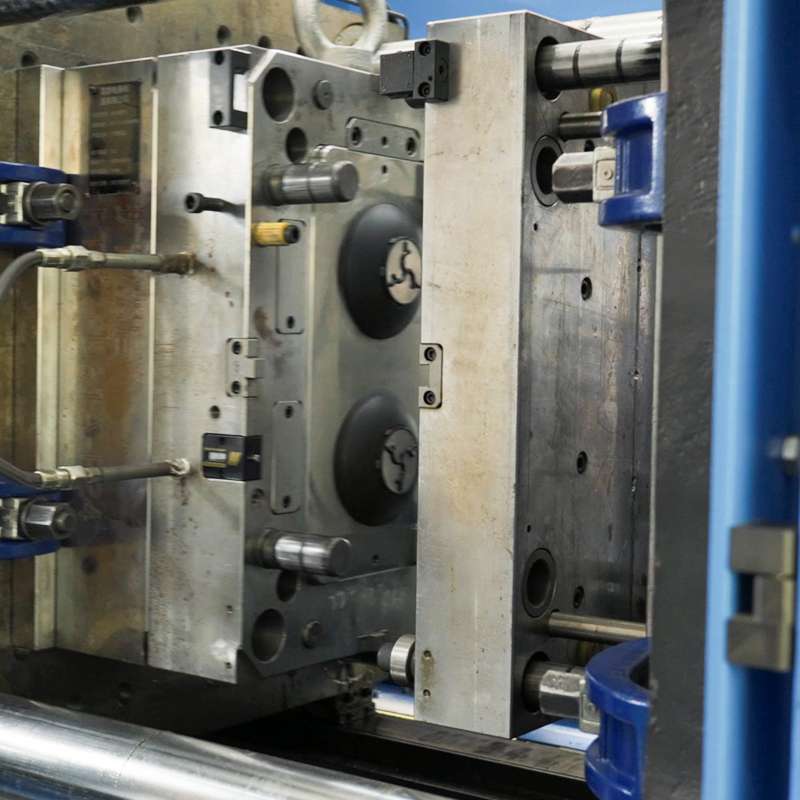
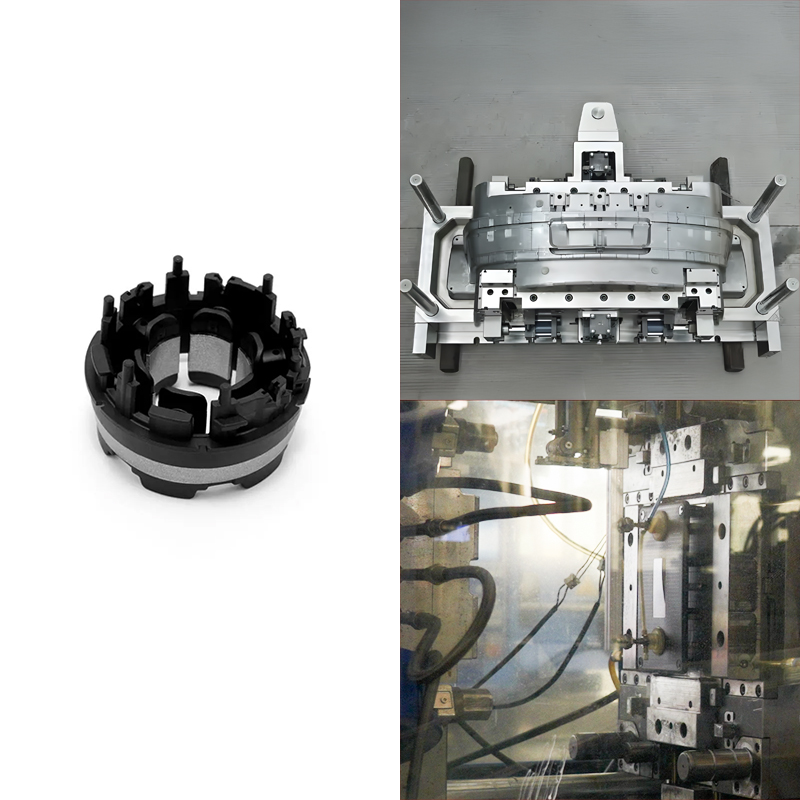
Injection molding for automotive parts is the process of injecting material in the molten form into a mold to create intricate parts mainly made of plastics. This technique is widely accepted in automotive manufacturing since it creates a high volume of parts with superior precision. The role of injection molding for automotive applications is characterized by effectiveness and versatility.
It lets manufacturers produce numerous automobile parts, external and internal, such as bumpers and panels, and internal and complex, like the dashboard and trims. In addition, it defines a process that has decreased the time and cost of production.
Injection molding has opened the use of different materials, such as lightweight plastics, that contribute to fuel consumption and reduce the vehicle’s total weight. As the automobile production system advances, injection molding remains an essential part of the growth process.
Just-in-time manufacturing is a timely and inexpensive production of parts. It is crucial to address the rapidly changing specifications for modern vehicles through inventions such as electric cars and advanced safety features.
Injection molding is vital in improving vehicles’ performance, look, and environmental impact within the automotive industry.
Overview of the Injection Molding in Automotive Parts Process
Injection molding in automotive parts starts with preparing the material, including plastic pellets or granules. While preparing these materials, technicians dry them to remove water moisture. They then mix the dye and other vital components the clients require into the dry pellets.
After preparation, technicians place the raw material in an injection molding machine. The mold heats the material so that it melts. They then aim the plastic droplets into a closed mold by applying considerable pressure to cover all crevices of the mold cavity or shape.
After the injection of melt, a cooling stage starts. Cooling occurs in the cooling channels in the mold through which coolant is circulated to freeze the plastic. After the material has cooled, it adopts the shape of the mold.
Technicians use the ejector pins or plates to eject the final part at this phase. The product proceeds to quality inspection to see whether there are any faults and to ascertain that the part is of the right quality.
In the automotive industry, injection molding is vital for creating robust, precise, and performance components. The sector has sophisticated shapes and geometries for different car parts. Injection molding helps achieve repeatability in production.

Critical Advantages of Injection Molding for Automotive Parts
Injection molding plays a crucial role in the manufacture of the motive parts. This method has several advantages over conventional manufacturing processes, such as efficiency.
High Productivity Efficiency
Among the main benefits of the injection molding process is its high productivity efficiency. It allows producing a large number of parts per time. This high production efficiency depends on the rapid cycle times and Automation.
After making the molds, injection molding can repeatedly manufacture the parts quickly. The production duration is low, a few seconds to a few minutes per shot, depending on the type of part and the plastic material.
The process requires minimal hand work, minimizing possible human errors. In addition to benefiting from high accuracy, automating the systems makes it possible to handle the feeding, injection, cooling, and ejection of materials. This approach, in turn, enhances production.
Гибкость конструкции
This manufacturing process provides almost limitless design freedom compared to other manufacturing processes. The flexibility of this manufacturing process involves geometric density, material density, and degree of personalization. Techniques such as multi-material or co-injection molding allow manufacturers to use different materials and produce parts with dissimilar features and properties.
For instance, integrating rigid thermoplastics with other softer touch materials can improve utility. The process enables customization, allowing manufacturers to create a distinct part ideal for a particular model of the car or customer.
Cost-Effectiveness
The first-time acquisition cost of the injection molding equipment and the creation of molds can be costly. However, there are more gains accrued from the process. Due to high initial expenses, injection molding has become economical for large-scale productions. In this manufacturing process, the cost per unit decreases as the number of units manufactured increases. This is an advantage for automotive part manufacturing.
One thing worth noting is the exhaustiveness of injection molding, as it only uses a few materials. Manufacturers can recycle the remains from the process, saving on the cost of raw materials.
Automating the process can significantly reduce labor costs by reducing the number of employees running the equipment.
Consistent Quality
Using injection molding in automotive parts produces high-quality products and increases consistency in subsequent production runs. All the parts are produced under similar circumstances, including the dimensions and parties of the parts. This reliability is critical in the emotive industry, where safety measures and high performance are essential.
Common Automotive Parts Produced through Injection Molding
The injection molding process allows the formation of complex shapes and confers precision and capacity to deal with higher production. It is appropriate for different elements of a car. Below is a list of common automotive parts made using injection molding:
Car Lights (Headlights and Tail Lights)
The clear plastic lenses in car head and tail lights are products of injection molding. Manufacture of these components requires a high degree of accuracy and clarity because of the importance of light transmission and safety. These lights should be able to sustain and endure impact and extreme weather conditions. Such conditions include frost, snow, rainfall, and scorching sunlight. The manufacturability requirements of injection molding enable one to freely design part thickness in amplitude and frequency, conforming to such densities.

Door Handles
Most door handles are injection-molded products, whether internal or external. The process allows for the refined shaping of the part and the integration of ergonomic design. Door handles must be robust and stylish since they play a high-cycle application. Injection molding allows for the possibility of combining materials. Manufacturers can use a rigid plastic base for the container and a softer material to manufacture the handle.

Бамперы
Automotive bumpers are large structural items that shield vehicles from impacts and are products of injection molding. The process is ideal for making buttressing parts critical to any car assembly. Car bumpers must be strong to protect the car in an accident. Proper selection of materials for the bumper is essential as it contributes to vehicle prices. Injection molding helps produce bumpers with the correct strength and with a high level of accuracy.

Приборные панели
Dashboards are large, multifaceted products of injection molding. They contain bezels, buttons, switches, dials, other indicators, and other safety components like airbags. Depending on the car type, the dashboard must have a pleasing finish and be strong enough to endure daily usage. As the name suggests, injection molding is a process of injecting material into a mold; hence, one can easily add several features under this process, producing a slippery surface.

Interior Trim Pieces
Injection molding forms the interior trim parts, including door panels, center console, and dashboard assimilators. These components make the vehicle’s interior attractive and have other uses. Trim pieces need to be light while being durable and able to adapt coordinated and contrasting textural, colored, and finishing elements. Injection molding also offers the integrality, aesthetic, and ergonomic performance necessary for such a style.

Решетки
Grilles have practical applications as cooling devices for the engine and conform to a part of the car’s facade design. Injection molding guarantees that these parts are durable and aesthetically appealing.
Air Vents and HVAC Components
Car interior vents and other parts of a car’s climate control system are common injection molding products. They require finer specifications to allow the optimal quantity of airflow and regulate the temperature. Injection molding makes it possible to create AC components.
Engine Covers
The engine covers are injection molded to shield essential parts of the engine from dirt and heat. These covers require proper seal material selection. They should be light in weight, heat-resistant, and long-lasting. Injection molding guarantees that it possesses these functional requirements while absolving the appearance of sleekness.
Fuse Boxes and Electrical Housings
Boxes and enclosures safeguard delicate electrical parts from physical collapse, humidity, and debris. All these parts require high accuracy and ability. Thus, injection molding is the preferred manufacturing process for these components. It also allows the use of ap-fit designs to construct the model for easy interconnection.
Wheel Arch Liners
Injection molding produces wheel arch liners. These liners cover the vehicle’s wheel arches and prevent them from coming into contact with mud, dirt, or debris. These parts must be sufficiently rigid and ductile to withstand daily exposure to acute road conditions. Conversely, they should be able to manage overloading the vehicle.
Pillar Garnishes
Injection molding produces the structural pillars of a vehicle interior garnished with Pillar garnishes. This process enables proper fitting and appearance. Such subassemblies play a role in the vehicle interior’s appearance and mask safety components such as airbags.
Types of material used in Automobile Injection Molding
Automotive injection molding can accommodate a variety of materials to produce a part that has desirable strength and heat resistance characteristics. Some examples are various types of plastics and composites that provide distinctive characteristics to satisfy a specific requirement of automobiles. Below is an overview of the common materials and their relevance to the automotive industry:
Полипропилен (PP)
PP is a thermoplastic type with extreme chemical stability, relatively low weight, and remarkable elasticity. It is common in automotive interior and exterior trims, including bumpers, dashboards, and door panels. It has a low density and high impact strength, which does not ensure the material cracks easily. PP is more cost-effective and mechanically superior to other polymers due to its flexibility and durability; hence, it is suitable in applications where subject parts experience heavy use.
Акрилонитрил-бутадиен-стирол (ABS)
ABS is a high-strength, highly durable thermoplastic with high toughness, impact strength, and excellent rigidity. A popular automotive application of ABS is interior trim parts, dash interventions, and consoles. Its shining surface makes it suitable for the appearance of automobile parts and other cars which call for polished parts. ABS is also common in automotive interior applications because of its fine appearance and high-impact strength.

Polyamide (Nylon)
Nylon has good mechanical properties, like wear resistance and high-temperature strength. It also has good chemical resistance to different automotive fluids, including oil and fuel. Nylon is common in many under-the-hood parts, including engine hoods, air intakes, and fuel system trims. Its high thermal and mechanical characteristics justify its application in parts with high temperature and mechanical loads.
Поликарбонат (PC):
Polycarbonate is well known for its high impact resistance and clarity; it is often used where the application calls for safety and clarity. It is lightweight yet highly robust, making it of much value in safety concerns. Other typical PC applications include automotive interior and exterior trim such as headlamp and tail lamp lens, sunroof, and panoramic roof. Polycarbonate is thus suited to producing parts that must be transparent and robust, such as automobile lighting fixtures.
Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE):
TPEs incorporate the attributes of plastics in processing while bearing the flexibility and elasticity of rubber. They give a good account of endurance, breakdown, and fluctuating temperatures. TPEs apply to seals, gaskets, and vibration-isolating components. They are helpful in parts where flexibility and high performance are desirable. TPE materials are necessary where the component has to have constant flexibility and dimensional stability concerning temperature. Possible application areas include doorsills and window channels.
Заключение
Injection molding is an essential technology for automotive parts production. It creates high-quality complicated parts accurately and quickly. Due to its flexibility, it is cheap and produces almost any part of the car.
The process caters to the increasing market for lightweight strength materials that can enhance vehicle dynamics and better fuel economy.
Technological advancements like Industry 4.0, Automation, and Additive manufacturing are essential in automotive injection molding. It improves efficiency and brings down costs, lead time, and an increase in quality.
The future seeks to launch advanced composites and bio-based plastics in the market, enabling the development of new lightweight and sustainable automotive structures. Furthermore, applying intelligent technologies and 3D printing to conventional injection molding will create new opportunities and additional variability.
Recommendation
To get more insight into some of the challenges and critical points in producing automotive parts, visit our “automotive parts manufacturing section”. This page provides an overview of many components for cars made through injection molding services, including lenses, door handles, and interior trims, etc.